Rare Earth Basics
Rare earth elements (REEs), or lanthanides, are a group of 15 elements in the periodic table with unique chemical, physical, and optical properties. Often included in this group is yttrium, which not only possesses similar characteristics to REEs, but is also frequently contained within the same mineral deposits. Although the elements themselves are found widely dispersed in the Earth’s crust, economic deposits are a rarity. These elements are only found with other REEs and do not occur individually.

Source: Callahan, Michael. PSU.edu. Web Blog. <http://www.personal.psu.edu/mjc5169/ext-text.html>
RARE EARTH FACTS
REEs enable many of the world’s most advanced technologies serving as key components in mankind’s quest for electronics miniaturization, energy efficiency, environmental stewardship, and technological advancement. While REEs have long played an underlying role in technology development, recent attention to global supply/demand dynamics and overall industry structure has brought their importance to the forefront. ~70% of all REEs are produced in China. This has raised concern around the world, particularly as China has taken steps to curb production–and exports–of these key elements.
Global Rare Earth Oxide(REO) Production Trends
U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries, Rare Earths, January 2025: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2025/mcs2025-rare-earths.pdf

Source: Gambogi, Joseph. “Global Rare Earth Oxide (REO) Production Trends,” U.S. Geological Survey. 16 April 2012. Web. <http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/rare_earths/ree-trends-2010.pdf>
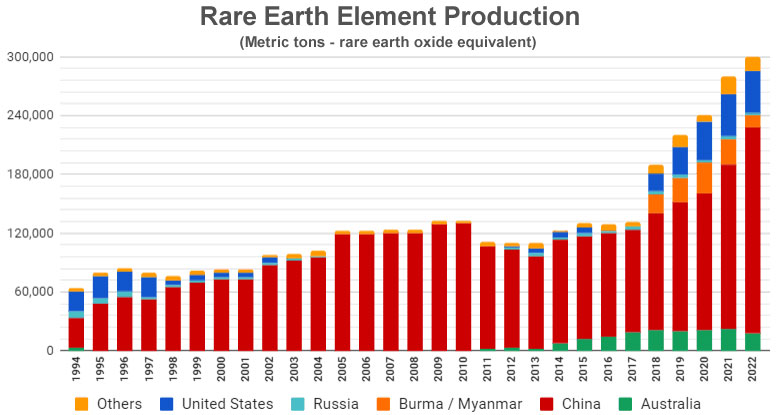
Source: Graph by Geology.com using data from the United States Geological Survey. https://geology.com/articles/rare-earth-elements/
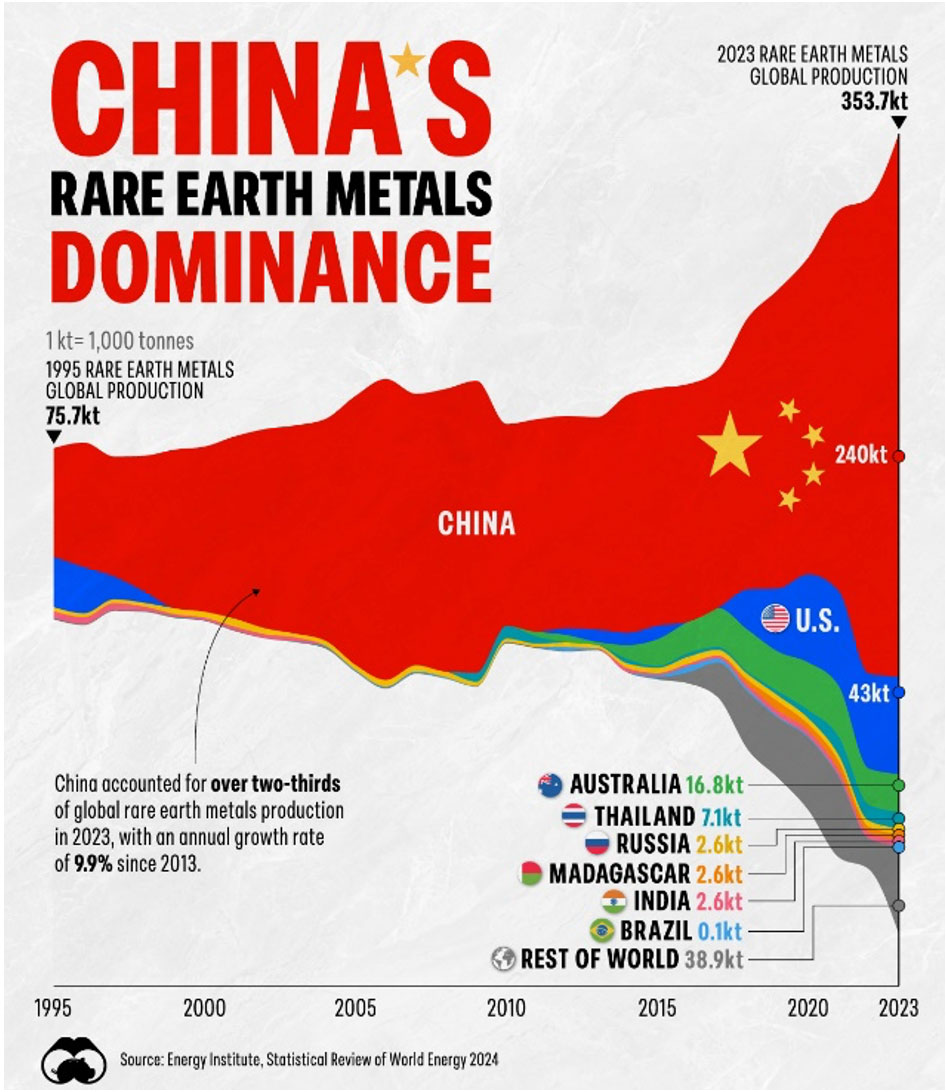
Visual Capitalist: Visualizing Global Rare Earth Metals Production (1995-2023): https://www.visualcapitalist.com/visualizing-global-rare-earth-metals-production-1995-2023/
REEs include the following:
|
|
|
|
|
LIGHT Vs HEAVY RARE EARTHS
REEs are often divided into Light Rare Earth Elements (LREEs) and Heavy Rare Earth Elements (HREEs) based on their chemical properties. Globally, LREEs are more abundant than HREEs, according to published sources, particularly in economic quantities and concentrations. As a result, HREEs tend to be far more valuable. REEs are integral to many common electronics such as cell phones and laptop computers.
During the past 20 years, many new applications for REEs have been developed and there has been an increase in demand for many items that require rare earth elements. For example, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) rechargeable batteries are made with rare earth compounds. These batteries are found in items that range from handheld electronics to hybrid and electric vehicles. Rare earth elements are also used in in flat screen displays, energy efficient lighting, lasers, and fiber-optic communication systems.
Typically, REEs are present only in small quantities. Large deposits, like Texas Mineral Resources’ Round Top project in Hudspeth County, Texas, are rare.
References Cited
Haxel, Gordon B., Hedrick, James B., and Orris, Greta J. ”Rare Earth Elements – Critical Resources for High Technology,” USGS.gov. May 17, 2005. Web. <http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2002/fs087-02/>
Investopedia Staff. ”Understanding Rare Earth Metals,” Investopedia.com. Web. <http://www.investopedia.com/articles/stocks/11/understanding-rare-earth-metals.asp#axzz1Ycxs5gIV>
King, Hobart M., Ph.D. ”REE – Rare Earth Elements and their Uses,” Geology.com. Web. <http://geology.com/articles/rare-earth-elements/>



